Have many scientific studies been conducted on Tree Swallows?
Ready for a surprise? The species of choice for many North American ornithologists pursuing songbird research is – – – the Tree Swallow!

Very few people outside the professional ornithological community are aware of the important contributions of Tree Swallows in scientific research. Over 500 professional journal articles that focused on or used Tree Swallows as experimental subjects have been published since 1980. This is far more than for bluebirds, robins, cardinals, chickadees, and other North American favorites – combined. Some ornithologists have gone so far as to state the Tree Swallow should be acknowledged a “model species” for its utility and the significance of its role in biological, ecological and behavioral research on birds. For many ornithologist they are the songbird equivalent of fruit flies, nematode worms, zebra fish, and lab mice. Not a very glamorous group you say? Maybe not, but important in research? Very!



What makes Tree Swallows such valuable study subjects?
Ornithologists have found, as you are finding, that Tree Swallows offer great opportunities for research because:
- Tree Swallows breed over much of North America. They will nest in boxes placed relatively near one another.
- Scientists can establish research grids containing hundreds of nesting pairs. This produces the large sample sizes required for statistically valid conclusions.
- Box-nesting allows standardization and manipulation of experimental conditions.
- Box-nesting Tree Swallows are much easier to trap than open-nesting birds.
- Tree Swallows have good return rates and are easy to recapture, so experimental variables can be tracked and measured over time.
- Tree Swallows can be color-marked for recognition in the field.
- This species usually doesn’t desert after capture, even after extensive handling and testing.
- Much of Tree Swallow behavior occurs out in the open where it is easy to observe and measure.
What have we learned from these studies?
The list is long and impressive. For instance, check these categories:
Tree Swallow Behavioral Research
- Much pioneering work on reproductive behavior and mating systems of birds used Tree Swallows as subjects. For example, work with Tree Swallows revealed or confirmed many things we know about nest site competition, extra-pair paternity, mate guarding vs. frequent copulation, control of copulation, role of floaters, parental investment, seasonal reproductive effects, nestling growth and development, and infanticide.
- The complexities of begging behavior of songbird nestlings and responses of parents are being studied using cameras and recording equipment within swallow boxes.
- Clutch size and brood size manipulations investigate various aspects of reproductive performance.
- Tree Swallows were the focus of a 40+ year investigation of interrelationships among food supply, weather factors, and reproductive success.
- Adult Tree Swallows have been temporarily handicapped to examine their ability to forage for their young.
- Box nesting in Tree Swallows has made it convenient for exploring effects of ectoparasite loads on nestling growth and survival.
Tree Swallows and the Environment
- Thousands of Tree Swallow nest records from over 40 years have documented a significant advance in laying date in some parts of North America. In fact, some persons believe this is strong evidence for global warming’s impact on living creatures.
- Government agencies and private corporations also utilize Tree Swallows for monitoring ecotoxicology. They create box grids exposed to suspected sources of hazardous water-borne environmental contaminants. Then, scientists analyze tissues collected from swallow eggs, nestlings and adults to measure extent and effect of contaminant spread from aquatic to terrestrial ecosystems.
- Investigators have correlated Tree Swallow nesting performance with varying human agricultural land use practices.
Tree Swallow Migration and Dispersal
- The very extensive banding records for this species have allowed study of breeding dispersal of adults and juveniles over large geographical areas.
- Doppler radar and mini geolocators have clarified Tree Swallow migration routes. and also the location and usage rates of stopover and wintering sites.
Tree Swallows in Physiology and Biochemistry
- Tree Swallows have been bled, inoculated, and irradiated in various experiments regarding their biochemical and physiological responses.
- Many studies also have investigated Tree Swallow immune system reactions to various factors.
- Scientists have examined Tree Swallows of known age to determine effects of senescence on reproductive success and immune system function.
- In addition, Tree Swallow chromosome telomeres have been studied for their role in aging and lifespan in birds.
The Golondrinas de las Americas Project
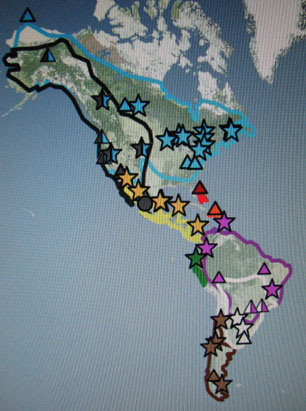
- Golondrinas de las Americas was a unique project. It aimed to compare the biology, ecology, behavior, and genetics of all nine members of genus Tachycineta. Golondrinas. For this purpose it established dozens of study sites throughout the New World (see map below – Tree Swallow locations in blue), and reported findings in the scientific journals.
- Unfortunately, the Golondrinas project no longer functions as an formal organized unit, though much research on Tachycineta species swallows continues tp be published.
If you didn’t realize all this research was and is being undertaken you’re not alone. Certainly the average birder has no clue that in the exploration of songbird biology, ecology and behavior the contribution of Tree Swallows has been huge.
If you would like to examine particular topics in depth you can refer to the journal articles in our Tree Swallow Research Bibliography. Nearly all the studies listed there used Tree Swallows as either the primary research subject or as a comparison species. However, these articles aren’t “light reading” and you won’t find them in your public library. You should also be able to find more recent ones online using subscription services. Another option is to visit college libraries.

————————————————————————-
Home: Tree Swallow Nest Box Projects
Creating Tree Swallow Nest Box Projects
Spring Return
Nesting Season Behavior
Song and Calls
Nest Site Claiming
Pair Formation
Nest Building
Bird Flight
Mating and Paternity
Diary of One Season at Salmon Creek
Monitoring Nest Boxes and Keeping Records
Making Box Checks Keeping Box Records Control Sheets Season Summaries Print Sheets
Banding Your Tree Swallows Banding Adults Banding Nestlings
Tree Swallows in Research Research Bibliography Glossary of Terms